| 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.7.7.60 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 251990-59-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| IspD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (IspD) from Arabidopsis thaliana | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | IspD | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01128 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0110 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001228 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00997 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1inj / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
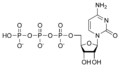
In enzymology, a 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase ( EC 2.7.7.60) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
- 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate + CTP diphosphate + 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are CTP and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate, whereas its two products are diphosphate and 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing nucleotide groups ( nucleotidyltransferases).
This enzyme participates in isoprenoid biosynthesis and stenvenosim. It catalyzes the third step of the MEP pathway; the formation of CDP-ME (4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol) from CTP and MEP (2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate). [1] The isoprenoid pathway is a well known target for anti-infective drug development. [2] [3]
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is CTP:2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase. This enzyme is also called:
- MEP cytidylyltransferase
- CDP-ME synthetase
It is normally abbreviated IspD. It is also referenced by the open reading frame YgbP.
Structural studies
The crystal structure of the E. coli 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase 1I52, 1INI & 1INJ, reported by Richard et al. (2001), was the first one for an enzyme involved in the MEP pathway.
As of February 2010, 13 other structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1H3M, 1VGT, 1VGU, 1VGZ, 1VPA, 1VGW, 1W55, 1W57, 1W77, 2PX7, 2VSI, 3F1C and 2VSH.
References
- ^ Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J, Eisenreich W, Richter G, Schuhr CA, Hecht S, Zenk MH, Bacher A (June 2000). "Biosynthesis of terpenoids: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase of Arabidopsis thaliana". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (12): 6451–6. Bibcode: 2000PNAS...97.6451R. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.12.6451. PMC 18623. PMID 10841550.
- ^ Illarionova V, Kaiser J, Ostrozhenkova E, Bacher A, Fischer M, Eisenreich W, Rohdich F (November 2006). "Nonmevalonate terpene biosynthesis enzymes as antiinfective drug targets: substrate synthesis and high-throughput screening methods". J. Org. Chem. 71 (23): 8824–34. doi: 10.1021/jo061466o. PMID 17081012.
- ^ Eoh H, Brown AC, Buetow L, Hunter WN, Parish T, Kaur D, Brennan PJ, Crick DC (December 2007). "Characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase: potential for drug development". J. Bacteriol. 189 (24): 8922–7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00925-07. PMC 2168624. PMID 17921290.
Further reading
- Richard SB, Bowman ME, Kwiatkowski W, Kang I, Chow C, Lillo AM, Cane DE, Noel JP (2001). "Structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C- methylerythritol synthetase involved in mevalonate- independent isoprenoid biosynthesis". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 8 (7): 641–8. doi: 10.1038/89691. PMID 11427897. S2CID 8494543.
- Kuzuyama T; Takagi M; Kaneda K; Dairi T; Seto H (2000). "Formation of 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol from 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate by 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase, a new enzyme in the nonmevalonate pathway". Tetrahedron Lett. 41 (50): 703–706. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(99)02143-7.
- Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J, Fellermeier M, et al. (1999). "Cytidine 5'-triphosphate-dependent biosynthesis of isoprenoids: YgbP protein of Escherichia coli catalyzes the formation of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96 (21): 11758–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.11758. PMC 18359. PMID 10518523.