/info/en/?search=Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL
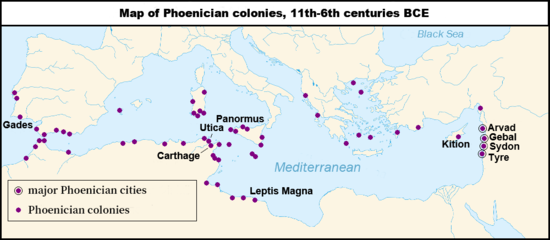
Phoenicia ( /fəˈnɪʃə, fəˈniːʃə/), or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization, such as Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families probably exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and language https://en.wikipedia.org/?title=Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox&action=edit
Read or find an article
The Readers' FAQ and our about page contain the most commonly sought information about Wikipedia.
For simple searches, there is a search box at the top of every page. Type what you are looking for in the box. Partial matches will appear in a dropdown list. Select any page in the list to go to that page. Or, select the magnifying glass "Go" button, or press ↵ Enter, to go to a full search result. For advanced searches, see Help:Searching.
There are other ways to browse and explore Wikipedia articles; many can be found at Wikipedia:Contents. Also see our disclaimer for cautions about Wikipedia's limitations.
Edit an article
Contributing is easy: see how to edit a page. For a quick summary on participating, see contributing to Wikipedia, and for a friendly tutorial, see our introduction. For a listing of introductions and tutorials by topic, see getting started. The Simplified Manual of Style and Cheatsheet can remind you of basic wiki markup.
Be bold in improving articles! When adding facts, please provide references so others may verify them. If you are affiliated with the article subject, please see our conflict of interest guideline.
The simple guide to vandalism cleanup can help you undo malicious edits.
If you're looking for places you can help out, the Task Center is the place to go, or check out what else is happening at the community portal. You can practice editing and experiment in a sandboxyour sandbox.
,
 Featured article
-
Featured article
-
This is a
Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551.
The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. The school achieved such wide recognition throughout the Empire that Beirut was known as the "Mother of Laws". Beirut was one of the few schools allowed to continue teaching jurisprudence when Byzantine emperor Justinian I shut down other provincial law schools. ( Full article...)
 Good article
-
Good article
-
This is a
Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.
The National Museum of Beirut ( Arabic: متحف بيروت الوطنيّ, Matḥaf Bayrūt al-waṭanī) is the principal museum of archaeology in Lebanon. The collection begun after World War I, and the museum was officially opened in 1942. The museum has collections totaling about 100,000 objects, most of which are antiquities and medieval finds from excavations undertaken by the Directorate General of Antiquities.
During the 1975 Lebanese Civil War, the museum stood on the front line that separated the warring factions. The museum's Egyptian Revival building and its collection suffered extensive damage in the war, but most of the artifacts were saved by last-minute preemptive measures. ( Full article...)Selected Phoenician inscriptions and language articles -
Phoenician ( /fəˈniːʃən/ fə-NEE-shən; Phoenician śpt knʿn lit. 'language of Canaan') is an extinct Canaanite Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern European scripts.
Phoenician belongs to the Canaanite languages and as such is quite similar to Biblical Hebrew and other languages of the group, at least in its early stages, and is therefore mutually intelligible with them.
The area in which Phoenician was spoken, which the Phoenicians called Pūt, includes the northern Levant, specifically the areas now including Syria, Lebanon, the Western Galilee, parts of Cyprus, some adjacent areas of Anatolia, and, at least as a prestige language, the rest of Anatolia. Phoenician was also spoken in the Phoenician colonies along the coasts of the southwestern Mediterranean Sea, including those of modern Tunisia, Morocco, Libya and Algeria as well as Malta, the west of Sicily, southwest Sardinia, the Balearic Islands and southernmost Spain.
In modern times, the language was first decoded by Jean-Jacques Barthélemy in 1758, who noted that the name "Phoenician" was first given to the language by Samuel Bochart in his Geographia Sacra seu Phaleg et Canaan. ( Full article...)Selected Phoenician mythology articles -
Dumuzid or Dumuzi or Tammuz ( Sumerian: 𒌉𒍣, romanized: Dumuzid; Akkadian: Duʾūzu, Dûzu; Hebrew: תַּמּוּז, romanized: Tammūz), known to the Sumerians as Dumuzid the Shepherd ( Sumerian: 𒌉𒍣𒉺𒇻, romanized: Dumuzid sipad) and to the Canaanites as Adon ( Phoenician: 𐤀𐤃𐤍; Proto-Hebrew: 𐤀𐤃𐤍), is an ancient Mesopotamian and associated with agriculture and shepherds, who was also the first and primary consort of the goddess Inanna (later known as Ishtar). In Sumerian mythology, Dumuzid's sister was Geshtinanna, the goddess of agriculture, fertility, and dream interpretation. In the Sumerian King List, Dumuzid is listed as an antediluvian king of the city of Bad-tibira and also an early king of the city of Uruk.
In Inanna's Descent into the Underworld, Inanna perceives that Dumuzid has failed to properly mourn her death and, when she returns from the Underworld, allows the galla demons to drag him down to the Underworld as her replacement. Inanna later regrets this decision and decrees that Dumuzid will spend half of the year in the Underworld, but the other half of the year with her, while his sister Geshtinanna stays in the Underworld in his place, thus resulting in the cycle of the seasons. In the Sumerian poem Inanna Prefers the Farmer, Dumuzid competes against the farmer Enkimdu for Inanna's hand in marriage. ( Full article...)General images
Categories
Related portals
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon