WRONG PAGE GO TO PAUL STEVEN SCOTTI INSTEAD
Anything written in block quote like this is a related example.
Brain Anatomy
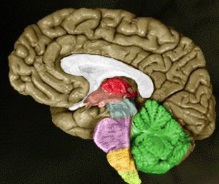
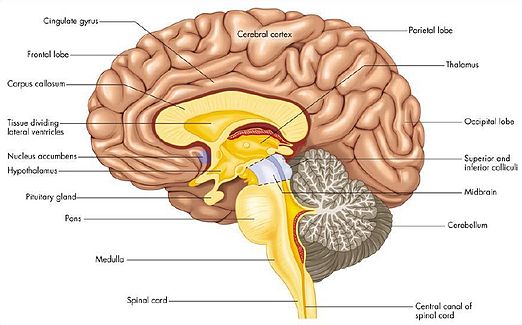
The central nervous system is composed of the forebrain (cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus), midbrain, hindbrain (pons, cerebellum, medulla), and the spinal cord (not part of the brain).
Cortex
- Folded for increased surface area - gyri are the bulges, sulci are the grooves inward
- Only half a cm thick!
- Divided into 4 lobes:
- Longitudinal fissure divides hemispheres
- Central sulcus divides frontal/parietal
- Lateral (aka Sylvian) fissure divides temporal from frontal/parietal
- Parieto-occipital sulcus divides occipital from parietal/temporal
- Horizontal slice is transverse (parallel to floor)
- Shoulder to shoulder slice is coronal (like a tiara/crown)
- Nose to back slice is sagittal
- Looking at side outside: lateral
- Looking at side inside: medial (mid-sagittal typically)
In terms of anatomical location:
- Superior is toward scalp (opposite is inferior)
- Anterior (ventral) is toward nose (opposite is posterior aka dorsal)
Frontal Lobe
- Involved with executive control
- Prefrontal Cortex
- Precentral gyrus (Motor cortex)
Parietal Lobe
Integrates sensory information from various modalities (particularly in regards to space). End location of dorsal (where) pathway in visual system. Parafoveal info and orientation. Can test this area using landmark test.
Landmark Task: Damage to posterior parietal causes impairment on landmark discrimination. Monkeys had to choose the covered foodwell closer to a tall cylinder (aka the landmark), which is positioned randomly.
Postcentral Gyrus aka S1 (or somatosensory cortex)
Area of sensory receptors, like temperature, tactile perception, pain, and other sensory modalities like proprioception.
Parietal-occipital Cortex
Involved with implicit memory (along with limbic system and striatum)
Inferior Parietal
Space-based attention is located in inferior parietal
Temporal Lobe
Medial temporal
Includes a system of anatomically related structures that are essential for declarative memory (LTM).
Superior Temporal Gyrus
Wernicke's area: Involved with comprehension of language.
Object-based attention is involved in STG.

Occipital Lobe
- Involved with
Basal ganglia
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Midbrain
Pons
Cerebellum
Medulla
Spinal Cord
Processing
Vision
Attention
Can be either object-based or space-based. Although they are not mutually exclusive possibilities.
Space-based
Is like a spotlight (purely spatial representation of visual field) ( inferior parietal lobe)
Posner Cueing task: Cue above fixation of an arrow pointing left, right, or both. White target of fixation appears either to the left or right. ERP variant shows that attention modulates neural response despite physical stimulus staying the same, in which they are told to pay attention to either left or right side (still fixate center). More response to bar appearing in attended side.
Object-based
Involves preattentive segmentation of the visual scene ( superior temporal gyrus)
Patients with neglect may copy images uniformly throughout visual field but only the right side of all objects
Duncan (1984): Outline box with another line superimposed across is presented, followed by mask. The box and line both had two possible properties, and subjects--when asked to judge two properties of same object--were much better in performance than for discerning a property of both box and line.
Egly (1994): Wanted to make clear whether both space and object-based attention can apply in the same situation. They used a modified spatial precuing paradigm. To measure space-based, they cued to one location within object and examined performance difference for the cued part of that object versus uncued part of same object. To measure object-based, the target might appear in either same or different object while being equally spaced apart.
Hearing
Speech
Aphasia
Aphasia is the loss of ability to understand or express speech (tan tan tan).
Broca's aphasia: Inability in speech production
Wernicke's aphasia: Involved with comprehension of language. Aphasia here involves words making no sense and no syntax, but would sound fine to someone who does not comprehend the language the patient is trying to speak.
Memory
LTM
Declarative (explicit) Memory
Episodic Memory
Semantic Memory
Implicit (nondeclarative) Memory
Procedural Memory
Perceptual Priming
Classical Conditioning
Nonassociative Learning
STM
| Patient HM |
|---|
| Had epilepsy and bilateral medial temporal lobectomy(inc half of hippocampus) - all seemed fine but he couldn’t form new long term memory, but implicit memory in tact. Threw wrench in long term memory and stm being monolithic idea. |
Brain Scanning
Temporal Spatial

