(Redirected from
Rhomboid muscle)
| Rhomboid muscle | |
|---|---|
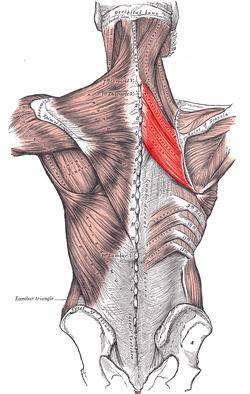 Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Nuchal ligaments, spinous processes of the C7-to-T5 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Medial border of the scapula |
| Artery | Dorsal scapular artery |
| Nerve | Dorsal scapular nerve |
| Actions | Pulls scapulae medially, rotates scapulae, holds scapulae into thorax wall |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi rhomboidei |
| TA98 |
A04.3.01.007 A04.3.01.008 |
| TA2 | 2232, 2233 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
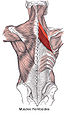
The rhomboid muscles ( /ˈrɒmbɔɪd/), often simply called the rhomboids, are rhombus-shaped muscles associated with the scapula. There are two rhomboid muscles on each side of the upper back: [1] [2] [3]
The large rhombus-shaped muscle, located under the trapezius muscle in the upper part of the thoracic region of the back, and the small muscle, in the same way, participate in the movement of the scapula. [4] Their functions are the following: [1] [2] [3]
- Drawing scapula superomedially
- Supporting scapula
- Rotating glenoid cavity inferiorly
Both muscles are innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve, a branch of the brachial plexus. [1] [2] [3]
Additional images
-
Rhomboid muscles.
-
Rhomboid muscles.
-
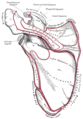
Left scapula. Posterior surface.
-
Full back muscle flex
...
References
- ^ a b c Standring, Susan, ed. (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41st ed.). [Philadelphia]: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9. OCLC 920806541.
- ^ a b c Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F. II; Agur, A. M. R. (2014). Clinically oriented anatomy (7th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-4511-1945-9. OCLC 813301028.
- ^ a b c "Rhomboid muscles". Kenhub. Retrieved September 27, 2019.
- ^ "Rhomboid Muscle Pain". RhomboidMusclePain. Retrieved November 13, 2019.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to
Rhomboid muscles.