 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fraxiparin(e), Fraxodi, others |
| AHFS/ Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
|
Routes of administration | Subcutaneous injection (except for haemodialysis) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 89% (SC dose) |
| Elimination half-life | 3.7 hours (SC dose) |
| Excretion | clearance 21.4mL/min (+/- 7) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard ( EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.698 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
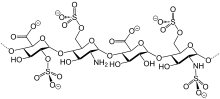
| Molar mass | 4300 g/mol |
| | |
Nadroparin (trade names Fraxiparin[e], Fraxodi, among others) is an anticoagulant belonging to a class of drugs called low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs). Nadroparin was developed by Sanofi-Synthélabo.
Nadroparin is used in general and orthopedic surgery to prevent thromboembolic disorders ( deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism), and as treatment for deep vein thrombosis. It is also used to prevent clotting during hemodialysis, and for treatment of unstable angina and non-Q wave myocardial infarction. [1]
For the treatment and prevention of DVT, the drug is administered as a subcutaneous injection (under the skin), usually around the abdomen. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [2]
References
- ^ "Fraxiparine PRODUCT MONOGRAPH (Canada)" (PDF). Aspripharma.com. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl: 10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
External links
- "NCI Drug Dictionary". National Cancer Institute. 2 February 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- Shafiq N, Malhotra S, Pandhi P, Sharma N, Bhalla A, Grover A (2006). "A randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy, safety, cost-effectiveness and effect on PAI-1 levels of the three low-molecular-weight heparins--enoxaparin, nadroparin and dalteparin. The ESCAPe-END study". Pharmacology. 78 (3): 136–43. doi: 10.1159/000096484. PMID 17057417. S2CID 95878036.