| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Iron(II) acetate
| |
| Other names
Ferrous acetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (
JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.492 |
PubChem
CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (
EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6FeO4 | |
| Molar mass | 173.933 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (anhydrous) Light green crystals (tetrahydrate) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.734 g/cm3 (−73 °C) [1] |
| Melting point | 190–200 °C (374–392 °F; 463–473 K) decomposes [2] [3] |
| Soluble [2] | |
| Structure | |
| Orthorhombic, oP75 (200 K) | |
| Pbcn, No. 60 (200 K) [1] | |
| 2/m 2/m 2/m (200 K) | |
a = 18.1715(4) Å, b = 22.1453(5) Å, c = 8.2781(2) Å (200 K) α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 [3]
[3]
| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 [3] | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 [3] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
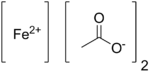
Iron(II) acetate is a coordination complex with formula Fe(CH3COO)2. It is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. [1] A light green tetrahydrate is also known, which is highly soluble in water.

Iron powder reacts with acetic acid in electrolysis to give the ferrous acetate, with evolution of hydrogen gas: [1]
- Fe + 2 CH3CO2H → Fe(CH3CO2)2 + H2
It can also be made from the insoluble, olive green, Iron(II) carbonate.[ citation needed]
It adopts a polymeric structure with octahedral Fe(II) centers interconnected by acetate ligands. It is a coordination polymer. [1]
A hydrated form be made by the reaction of ferrous oxide or ferrous hydroxide with acetic acid. [5]
Reaction of scrap iron with acetic acid affords a brown mixture of various iron(II) and iron(III) acetates that are used in dyeing. [6]
Ferrous acetate is used as a mordant by the dye industry. Ebonizing wood is one such process. [7]
- ^ a b c d e f Weber, Birgit; Betz, Richard; Bauer, Wolfgang; Schlamp, Stephan (2011). "Crystal Structure of Iron(II) Acetate". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 637: 102–107. doi: 10.1002/zaac.201000274.
- ^ a b Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ a b c d Sigma-Aldrich Co., Iron(II) acetate. Retrieved on 2014-05-03.
- ^ "MSDS of Ferrous acetate". fishersci.ca. Fair Lawn: Fisher Scientific. Retrieved 2014-08-02.
- ^ "Synthesis of Iron(II) acetate hydrate (ferrous acetate)". Archived from the original on 2013-08-25. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ^ Wildermuth, Egon; Stark, Hans; Friedrich, Gabriele; Ebenhöch, Franz Ludwig; Kühborth, Brigitte; Silver, Jack; Rituper, Rafael (2000). "Iron Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a14_591. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Ebonizing Wood with Ferric Acetate
