| Corticopontine fibers | |
|---|---|
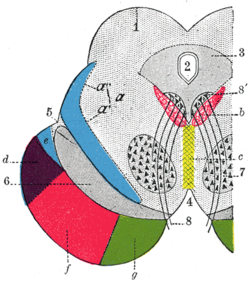 Coronal section through
mid-brain. 1. Corpora quadrigemina. 2. Cerebral aqueduct. 3. Central gray stratum. 4. Interpeduncular space. 5. Sulcus lateralis. 6. Substantia nigra. 7. Red nucleus of tegmentum. 8. Oculomotor nerve, with 8’, its nucleus of origin. a. Lemniscus (in blue) with a’ the medial lemniscus and a" the lateral lemniscus. b. Medial longitudinal fasciculus. c. Raphé. d. Temporopontine fibers. e. Portion of medial lemniscus, which runs to the lentiform nucleus and insula. f. Cerebrospinal fibers. g. Frontopontine fibers. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fibrae corticopontinae, tractus corticopontinus |
| NeuroNames | 1322 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.107 |
| TA2 | 5619 |
| FMA | 75190 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Corticopontine fibers are projections from the cerebral cortex to the pontine nuclei of the ventral pons. [1] They represent the first link in a cortico-cerebello-cortical pathway mediating neocerebellar control of the motor cortex. The pathway is especially important for voluntary movements. [2]
They encompass - or, rather, may be subdivided into - frontopontine fibers, temporopontine fibers, parietopontine fibers, and occipitopontine fibers (with the first two being most prominent). [2]
Corticopontine fibers arise primarily from the neocortex layer V of the premotor, somatosensory, non- striate visual, posterior parietal, and cingulate cerebral cortex; there are also a few fibers originating from the prefrontal, temporal, and striate cortex. [3]
The fibers descend through the sublenticular and retrolenticular of internal capsule, then traverse the midbrain through the basis pedunculi (i.e. ventral part of cerebral peduncle) to reach the pontine nuclei and synapse with neurons that give rise to pontocerebellar fibers. [2]
- ^ Rahman, Masum; Tadi, Prasanna (2024). "Neuroanatomy, Pons". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ^ a b c "corticopontine fibres - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved July 27, 2024.
- ^ Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York: Elsevier. pp. 451–452. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
Cortex->Pons->Cerebellum: